REGION: CONCEPT,CHARACTERISTICS AND CLASSIFICATION:
A Region is an area having uniform characteristics , On the other hand The Term of Region may be defined as different characteristics of between two regions according to specific criteria.A region may be stated as a sub areas within a nation.The greater development of sub area will be effected on nations.
SOME NOTABLE DEFINITION OF REGION GEOGRAPHERS:
HERBERTSON (1905) opines a region as" a complex of land ,water , air,plant,animals,, and man ,regarded in the spatial relationships as together constituting a definite portion of earth surface."
ARONVICI defines region as "a geographical area or areas which a given civilization standard
of a people seems to require for the fulfillment of its aspirations through material resources".
JEORG defines region, ’’any portion of the earth’s surface'where physical conditions are
homogeneous, is considered as region".
AMADEO defined, as a region as a set of location units homogeneous with respect to their values on a particular set of characteristics”.
Therefore there are various concept of region.No matter which concept is more important than other ,so that concept of region is very much dynamics stated by different geographers at various ways.
BACKGROUND AND HISTORY:
The root of the concept of region was originated in USA and in EUROPE.The concept of region was first given in 19th century by French geographer Vidal_ da _ la_ blache. He mainly gave two concept i.e milieu and pays .the pays was a local region and milieu was natural environment.
In 1920s and 1930s the geographers were more concentrated on the place,thinking about the similarities and dis similarities between two regions.
REGIONAL CHARACTERISTICS:
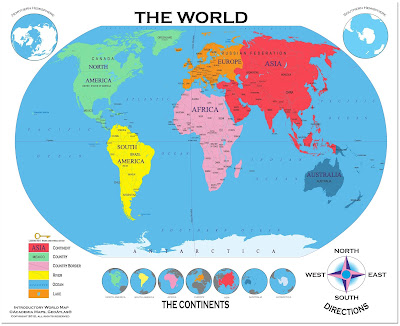
- A Region have a specific location that demarcated a region is different from others i.e. Asia ,Africa, South America, North America and Australia.
- The Thar desert, The Sahara desert have their particular spatial extension which identified them
- Region have a specific boundary that separates one region to other.
- A Region can be formal or functional.a formal region is a area in which uniform nature and functional region explains a function of a particular region.
- A Region have a transitional boundary.as A region is overlapping with other region.
CLASSIFICATION OF REGIONS
The regions is classified as follows
Physical Characteristics:
- Climate region
- Land form
- Natural vegetation
- Ecosystem
- Climate region
- Land form
- Natural vegetation
- Ecosystem
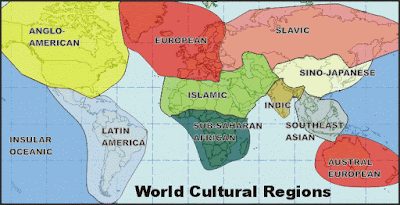
Cultural Characteristics:
- Population region
- Linguistic region
- Religious region
- Agricultural region
- Industrial region
- Transport and Trade
- Political region
- Economics region
- Natural region
- Urban region